What is CGM and How Does it Help Manage Diabetes?
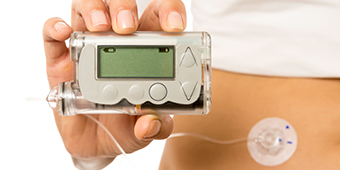
Continuous Glucose Monitoring or CGM is a method used by diabetes to regularly record and monitor their blood sugar levels. This is especially important for those who have insulin-dependent diabetes – those whose pancreas produces very little or no insulin at all.
All people with type 1 diabetes are insulin dependent.
Some people with type 2 diabetes are insulin dependent.
By injecting insulin into the body, you are able to better regulate your blood sugar levels when your body is no longer able to do so. Either insulin is injected into the body several times throughout the day or you might wear an insulin pump, which supplies insulin continuously.
The balance of insulin is very important – too much insulin and you could experience hypoglycemia, a very low blood sugar level. Too little insulin and you could experience hyperglycemia, a very high blood sugar level.
If you often have very low or very high blood sugar, you are at risk for damage to your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. You are also at risk for dizziness, falls, and other injuries.
How does CGM work?
Unlike conventional blood sugar monitoring where you have certain times each day that you prick your finger and feed it into a glucose monitor to see your level, Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) monitors your blood sugar all day long without a finger prick.
You may still need to do a finger stick when you have a CGM alert.
CGM systems uses a thread-like sensor, which is inserted into your subcutaneous fat tissue to measure interstitial fluid (not blood serum). Throughout the day and night, the sensor measures the sugar levels in your tissues and transmits the information to the monitoring device.
As you continue to wear the device and check your blood sugar variations each day, you can start to understand the effects of food, exercise, illness, and medication. This helps you better plan your days and better regulate your blood sugar levels.
Some people benefit from wearing a CGM because it alerts them to high or low blood sugars that might be missed during your regular finger stick blood sugar testing.
If you also wear an insulin pump, you can get CGM systems that work together with your insulin pump. The CGM transmitter will communicate throughout the day as you continue to also receive insulin.
Studies have shown that continuous glucose monitoring is beneficial for many patients because patients get regular blood sugar readings without needing a finger stick.
Talk to your healthcare provider about CGM to determine if it would be a good method of glucose monitoring for you. You can check with your insurance company to see if CGM is covered, then talk to your provider or endocrinologist for a prescription.
If you need an endocrinology specialist, call Beebe Endocrinology: 302-648-7999.
If you need more information or support with understanding your device or managing your diabetes symptoms, call Beebe Diabetes Management at 302-645-3121.



