Quality and Safety at Beebe Healthcare
Quality of patient care is multi-dimensional; it encompasses safety, timeliness, effectiveness, equity, efficiency, and patient-centeredness. Beebe Healthcare’s vision to be the health system of choice for all people in Sussex County promotes person-centered care delivery, evidence-based clinical practice, sustainable and high-value care models, alignment in incentive structures, and reformed healthcare design to achieve health equity.
Optimal quality comes from designing systems and processes in a way to make it easier for the health care workforce to achieve desired quality outcomes through continuous learning. Beebe Healthcare fosters a culture of continuous learning by taking a respectful, supportive, and responsive approach in its management systems across the entire organization, enabling the healthcare workforce to skillfully identify problems, as well as adopt and launch solutions that work best, thereby continuously delivering quality services that are highly reliable and sustainable to meet the needs of patients, populations, and communities in times of both stability and crisis.
Beebe’s Strategic Goals serve as a foundation for delivering the highest quality of care to our patients, populations, and community:

Beebe Healthcare's values include providing the highest quality care and experience for our patients. To support our commitment to transparency and promote accountability to our community's well-being, we are sharing quality and safety outcome results that help drive improvement in caring for our patients. Also listed are certifications, accreditations, designations, awards, and accolades that reflect the deep commitment Beebe Healthcare has for all patients to receive highly reliable, quality care.
Medication Error Rate
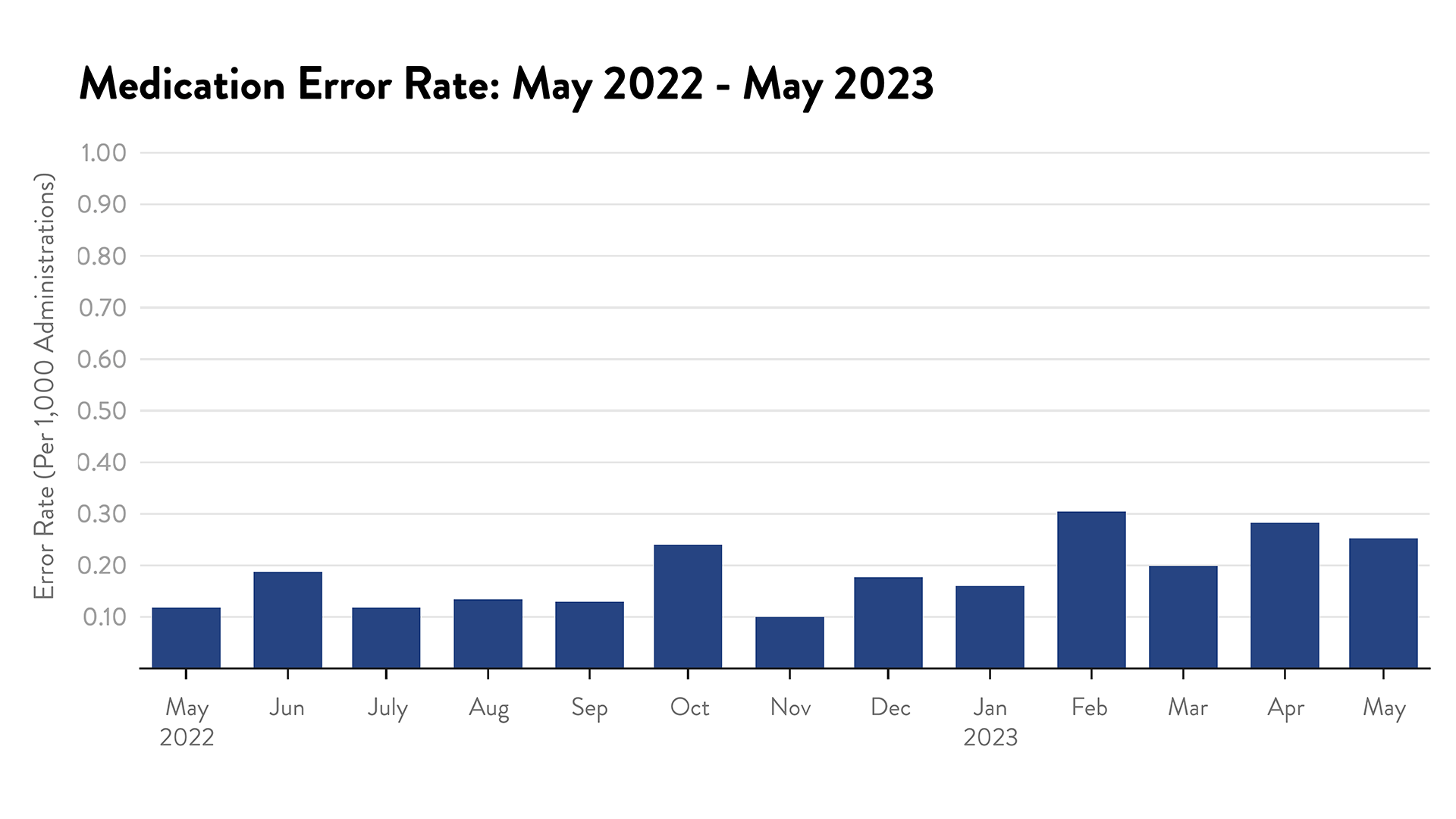
A medication error is defined as "any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm while the medication is in the control of the healthcare professional, patient, or consumer,” according to the National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. Medication errors can occur throughout the medication-use system. Beebe uses several methods to reduce this type of error, including:
- Bar Code Medication Administration Technology
- Tall Man Lettering, where part of a drug’s name in uppercase letters to help distinguish sound-alike, look-alike drugs from one another
- Allergy alerts in the electronic medical record for all patients
- SBAR communications (S-Situation, B-Background, A-Assessment, R-Recommendation) communications to inform doctors, nurses, and others who prescribe or administer medications about changes
- Describing medication errors in Daily Safety Huddles, with specific actions for prevention of the same type of error from occurring in the future
- Educating staff through newsletters, web-based training sessions, and clinical educator analysis of errors
- Electronic medical record alerts for physicians upon entering orders, to prompt review and analysis which helps eliminate wrong drug, wrong dose, duplicate dosing, and more
Bar Code Medication Administration (BCMA)
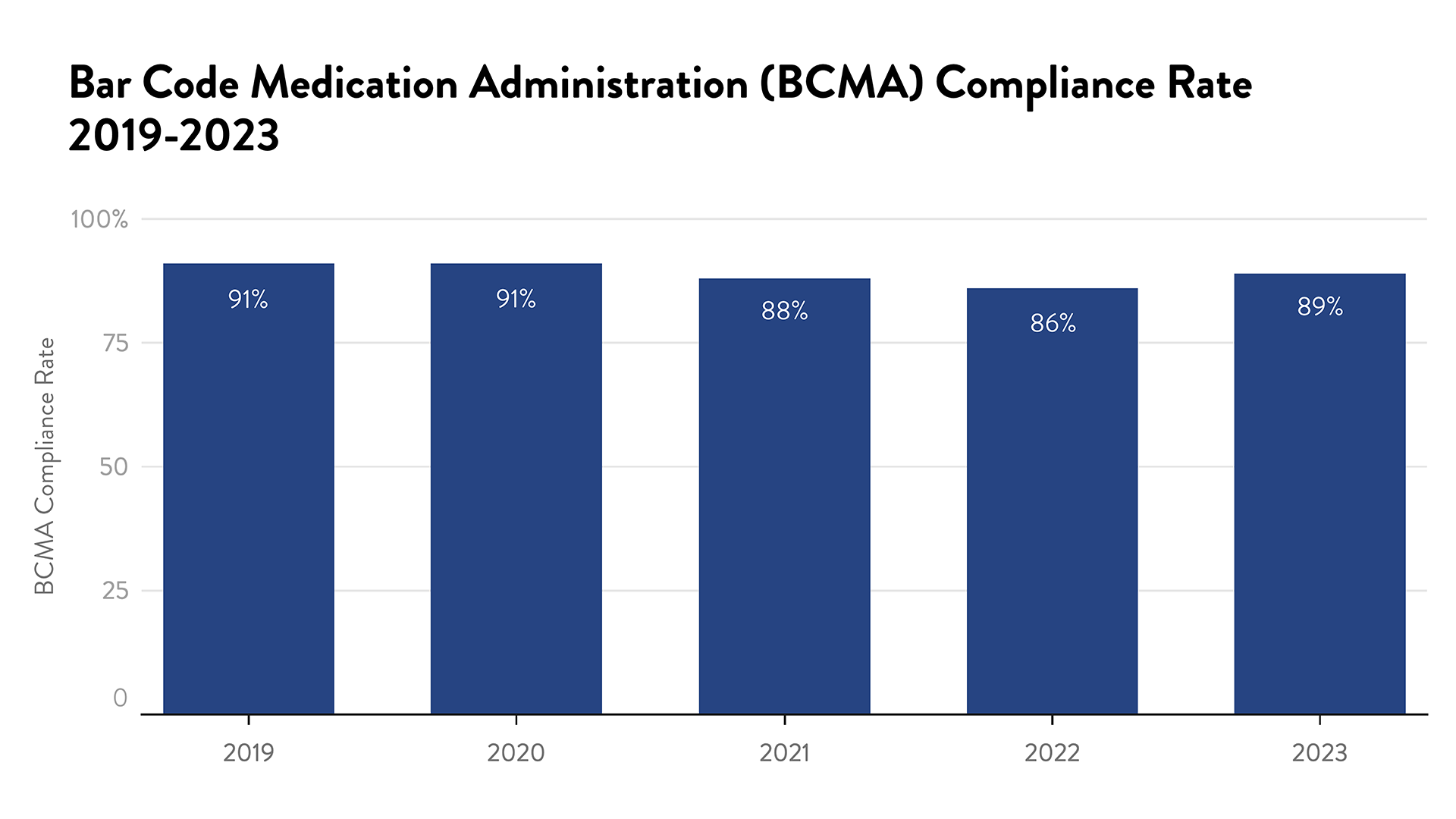
Barcode medication administration (BCMA) technology is a health information technology used to prevent medication errors and promote patient safety. Caregivers scan the barcode on the medication and the patient's identification wristband. This helps nurses confirm ‘five rights’ of medication administration: right patient, right medication, right dose, right route and right time. The BCMA has shown to reduce medication administration errors significantly and to reduce harm from serious medication errors.
At Beebe, nursing leadership has set compliance goals of 100% for patient scanning and 98% for medication scanning. To achieve these goals, nurse managers utilize an electronic report that provides unit, nurse, patient, and medication compliance rates. Additionally, direct observations are done on each unit and, if needed, immediate education is performed.
Bedsores: Hospital Acquired Pressure Injuries
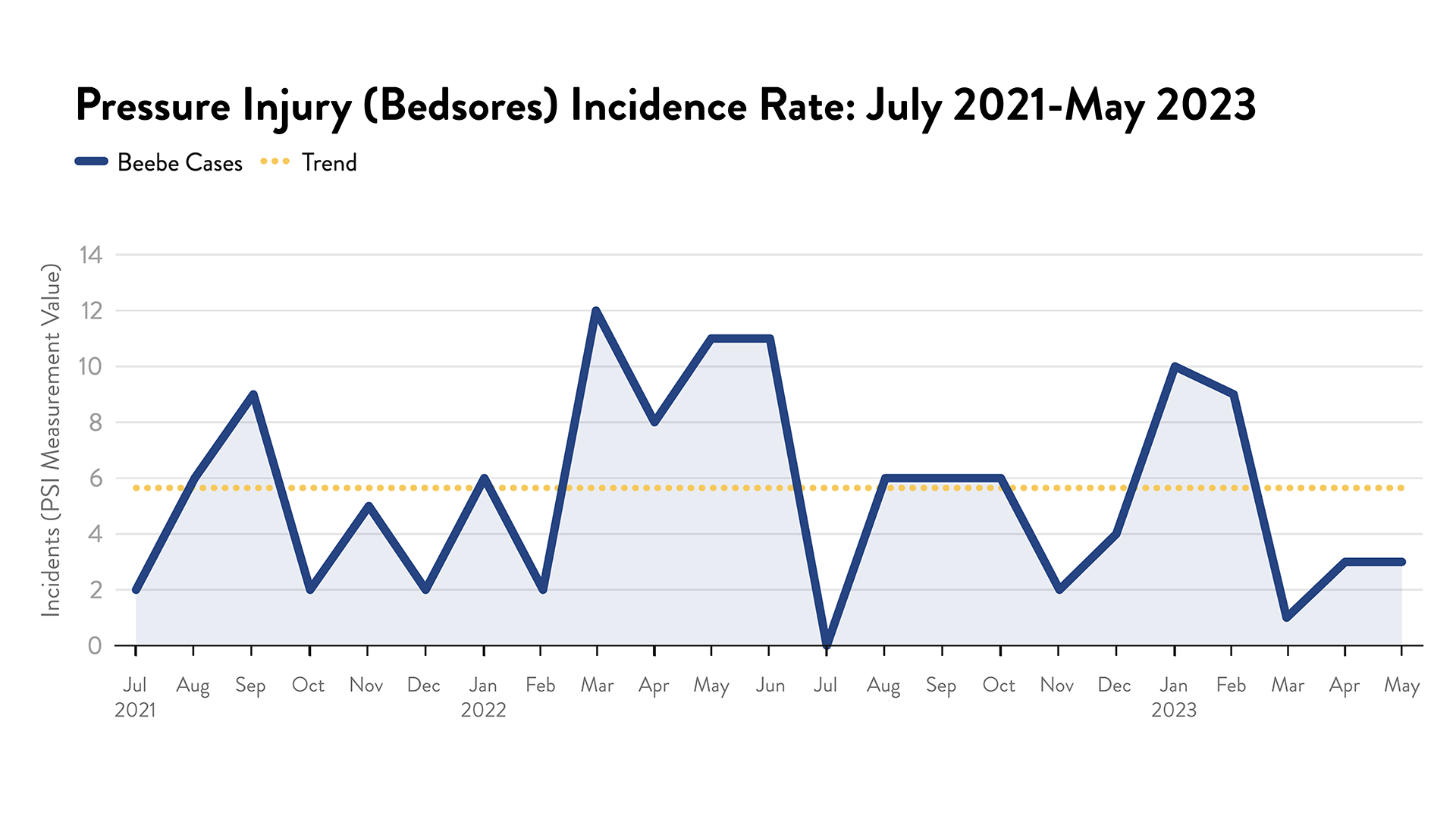
Commonly known as bedsores, pressure injuries are wounds in the skin or underlying tissue caused by pressure, friction and moisture. These injuries often happen when patients with limited mobility are unable to change positions. These injuries can damage the skin and muscles, slow recovery, and cause pain, infection and other problems.
Beebe Healthcare uses several measures to help prevent these injuries. Caregivers practice strict adherence to a schedule to turn/reposition patients at risk for pressure injuries at least once every two hours. These patients are also given special beds that reduce the likelihood of skin breakdown. In addition, Beebe has implemented Electronic Health Record “Camera Capture” to document the condition of a patient’s skin upon arrival to the hospital, during the admission, and throughout the time the patient spends in the hospital. This documentation enables early intervention to prevent skin breakdown. Beebe has also implemented a pilot of an electronic alert system that notifies staff when the patient needs to be turned. This device can also gauge the effectiveness of the turn/repositioning for optimal prevention of skin breakdown.
CAUTI: Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection
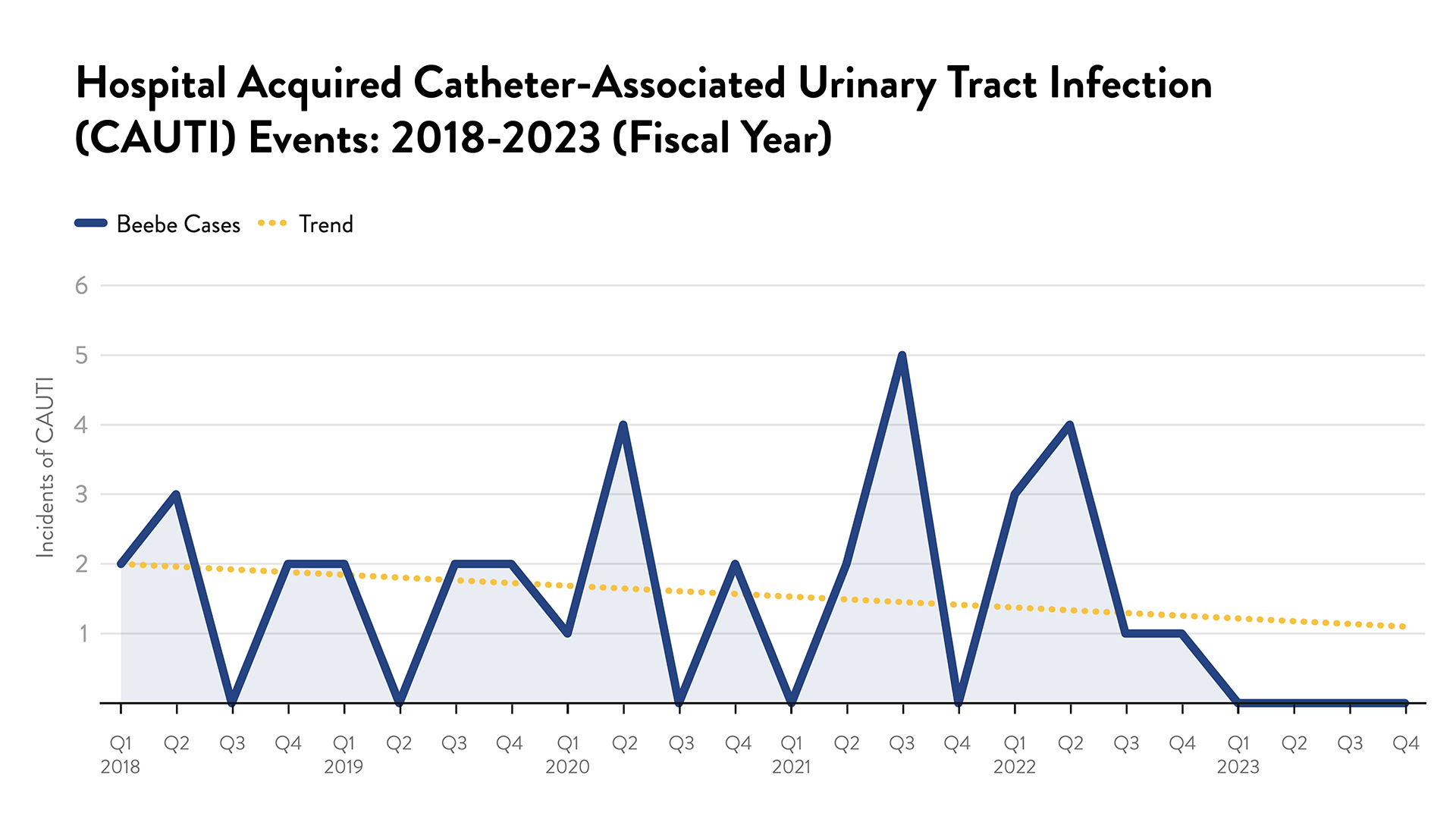
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection involving any part of the urinary system, including urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidney. UTIs are the most common type of healthcare-associated infection, and the vast majority of these infections are associated with a urinary catheter, which is a tube inserted into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine. Between 15-25% of hospitalized patients receive urinary catheters during their hospital stay. The most important risk factor for developing a catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is prolonged use of the urinary catheter. Therefore, catheters should only be used for appropriate indications and should be removed as soon as they are no longer needed.
In order to reduce these types of infections, Beebe has introduced purposeful rounding by nursing leaders, educators and Infection Prevention to ensure best practices are used. This rounding helps ensure standards are met for catheter insertion, care, and prompt removal.
C. Diff
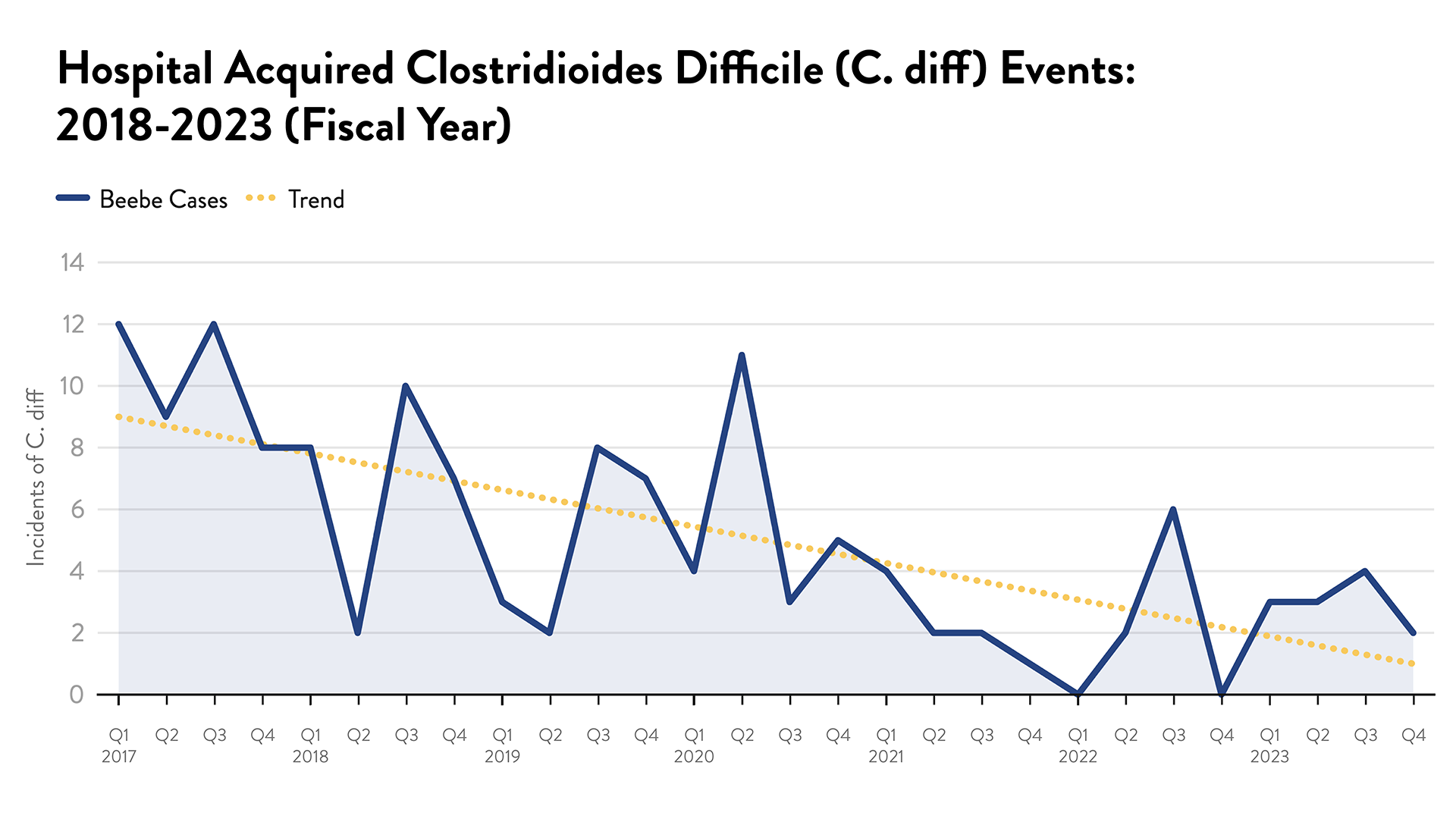
C. diff (also known as Clostridioides difficile or C. difficile) is a bacteria that causes diarrhea and colitis. Almost half a million infections in the United States each year are caused by this bacteria. Measures Beebe Healthcare is taking to reduce C. Diff infection rates include:
- reducing the use of unnecessary antibiotics
- "just in time" education for nursing and providers to ensure appropriate ordering of C. Diff tests
- incorporation of new room cleaning and disinfection products/technologies
CLABSI: Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection
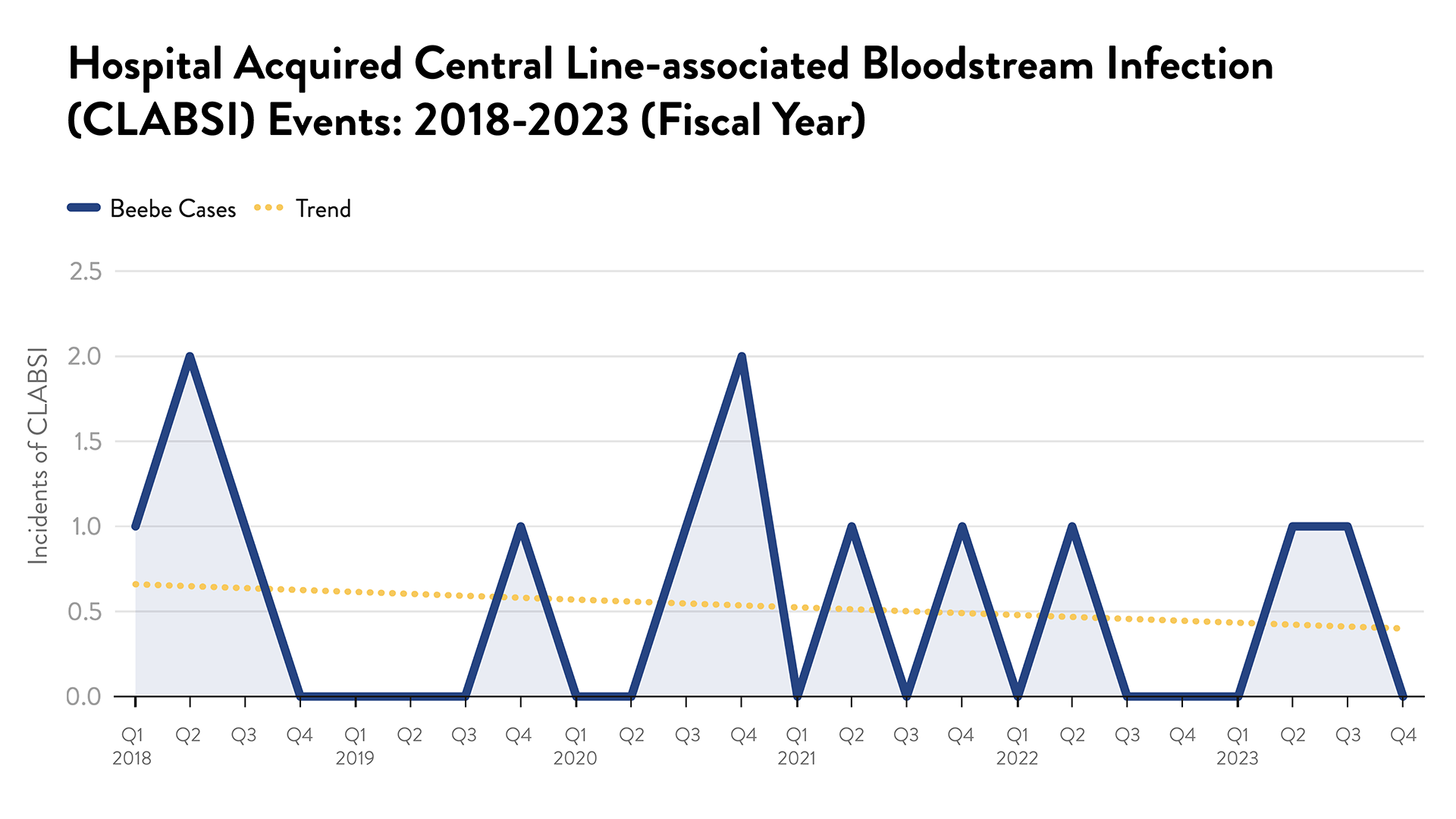
A central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) occurs when bacteria or other germs enter the patient's central venous catheter and then enter into their bloodstream. These infections are serious but can often be successfully treated. Beebe has expanded its use of protective caps containing a disinfectant on central lines, to include dialysis catheters.
MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
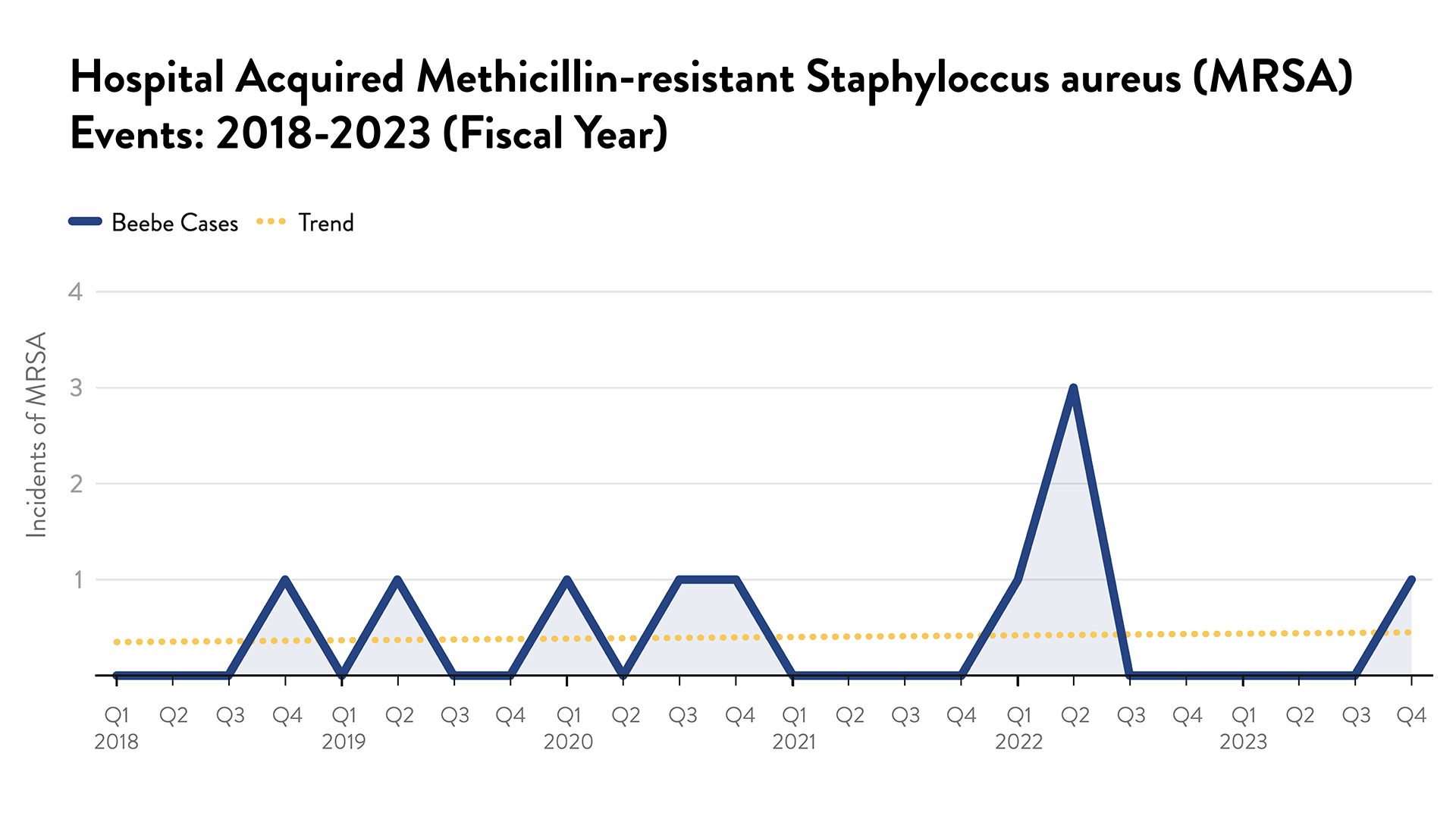
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is caused by a type of staph bacteria that's become resistant to many antibiotics. Most MRSA infections occur in people who've been in hospitals or other health care settings, such as nursing homes and dialysis centers. To further reduce CLABSI events, Beebe has expanded its use of disinfectant caps, which are designed to provide continuous protection against microbial contamination, to include dialysis catheters, a specific type of central line.
Fall Rates
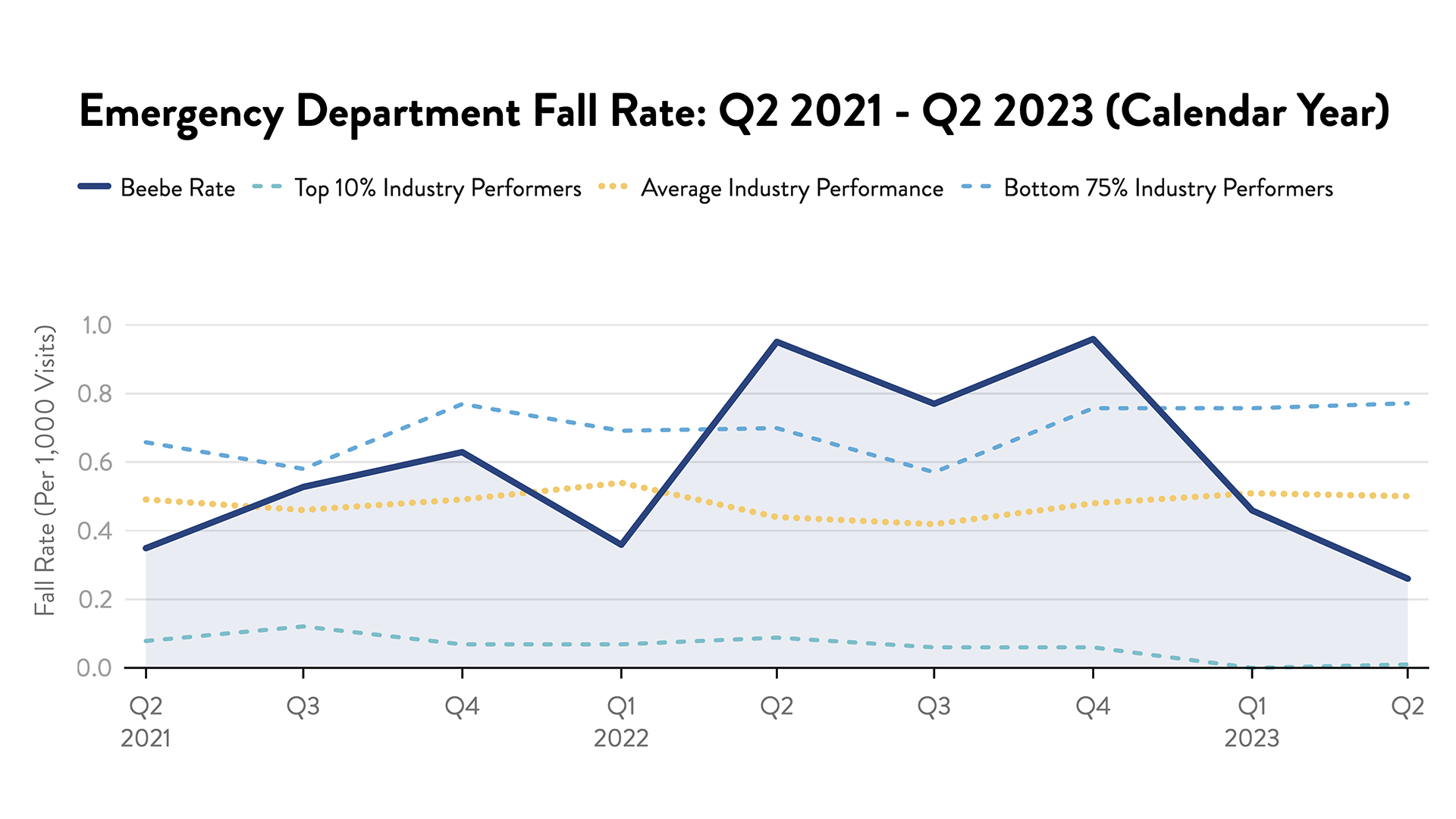
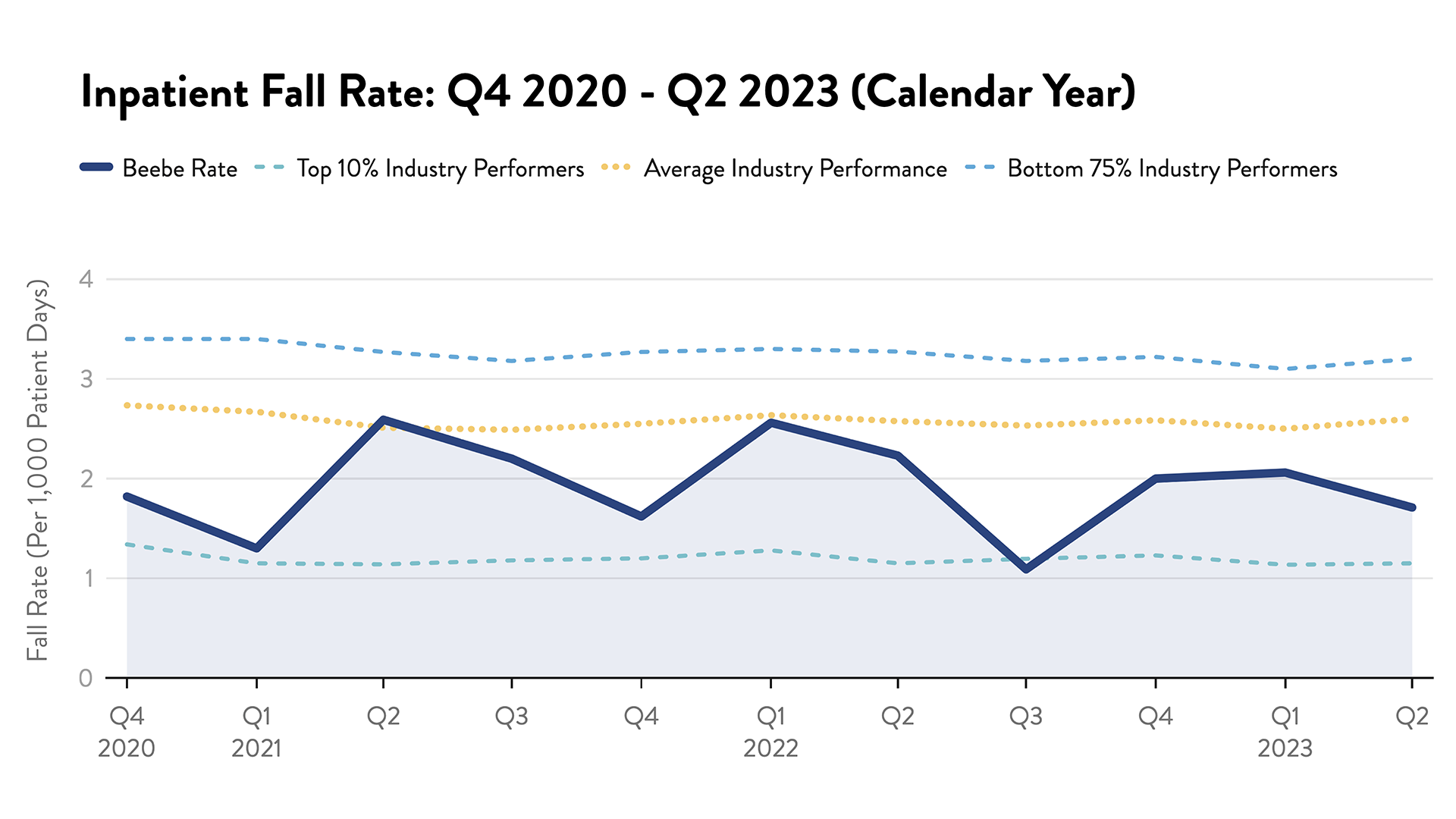
Each year, somewhere between 700,000 and 1,000,000 people in the United States fall in the hospital. A fall may result in fractures, lacerations, or internal bleeding, leading to increased healthcare utilization. To prevent falls, Beebe uses purposeful rounding. Caregivers round hourly on patients to assist with toileting and other tasks, ensuring patients with mobility issues have assistance. Caregivers also identify patients who may be at a higher risk for fall using a standardized scoring methodology. Patients are reminded “Call Don’t Fall." Many patients do not want to “bother” nurses, but are consistently reminded it's best to call a caregiver when you need assistance.










